Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Learn more
Last Updated on February 12, 2024 by Rhyes Frank
A furnace that frequently turns on and off, a condition known as short cycling, can be a significant concern for homeowners. This erratic behavior often signals underlying issues requiring prompt attention.
The most common cause of short cycling is a malfunctioning thermostat. When a thermostat is broken or not properly calibrated, it can misread the temperature, leading to the furnace turning on and off more often than necessary.
Another key factor is a dirty air filter. When the air filter is clogged, it restricts airflow, causing the furnace to overheat and shut down prematurely.
Similarly, obstructed air vents or a dirty blower wheel can lead to inadequate airflow, triggering the furnace to turn off to prevent overheating.
Short cycling can also be a symptom of more significant furnace problems, like issues with the furnace’s limit switch, which acts as a safety mechanism.
In gas furnaces, frequent cycling might indicate the need for a reset or signal issues with the ignition system. For electric heaters, repeated on-off cycles can point toward electrical problems.
Why Your Furnace Turns on and off and How To Fix It
1. Malfunctioning Thermostat
A thermostat acts as the command center for your furnace, regulating the heating cycle. When it malfunctions, it can cause the furnace to turn on and off irregularly. This can be due to improper placement, where it’s exposed to direct sunlight or drafts, leading to false temperature readings. It might also be due to internal faults, such as wiring issues or a depleted battery.
Solution: To fix a malfunctioning thermostat, first check its placement. Ensure it’s in a neutral location, away from direct heat sources or drafts. If placement isn’t the issue, inspect the thermostat for loose wiring and replace batteries if necessary. If these steps don’t resolve the problem, you may need to replace the thermostat.
2. Clogged Air Filters
Air filters trap dust and debris, ensuring clean air circulates through your HVAC system. Over time, these filters can become clogged, restricting airflow. This decreased airflow can cause the furnace to overheat and shut down prematurely to prevent damage, leading to short cycling.
Solution: Regularly check and replace your furnace’s air filters. This is a simple yet effective way to prevent many furnace issues, including short cycling. The frequency of replacement depends on your filter type and environmental factors, but a general rule is to check them every 1-3 months.
3. Overheating Due to Restricted Airflow
Apart from clogged air filters, other factors can restrict airflow, such as blocked vents or a dirty blower wheel. This restriction can cause the furnace to overheat and turn off as a safety measure.
Solution: Ensure all vents in your home are open and unobstructed. Regularly clean and maintain the blower wheel and other internal components of your furnace. If the problem persists, consult a professional, as the issue may be with the furnace’s internal mechanics.
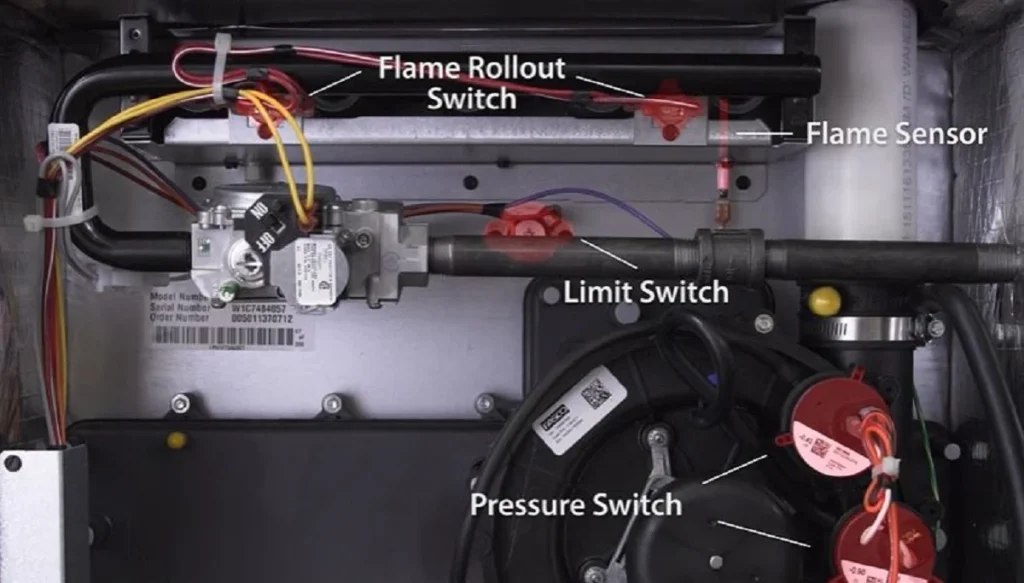
4. Faulty Flame Sensor
In gas furnaces, the flame sensor detects whether the burner has ignited. If it’s dirty or faulty, it may fail to sense the flame, causing the furnace to shut off as a precaution.
Solution: Carefully clean the flame sensor using a fine abrasive pad. If cleaning doesn’t work, the sensor may need to be replaced. This is a delicate component, so consider hiring a professional for repair or replacement.
5. High Limit Switch Issues
The high limit switch monitors the furnace temperature to prevent overheating. If this switch is malfunctioning, it can cause the furnace to shut off unexpectedly.
Solution: Check if the high limit switch is tripped and reset it if necessary. If the switch frequently trips, it might indicate a deeper issue, such as an oversized furnace or a problem with the heat exchanger. In such cases, professional assessment and repair are recommended.
Read More: Solving the Problem of Your Furnace Not Kicking On When Temperatures Drop
Short Cycling’s Effect on Furnace Health
Short cycling, where a furnace rapidly turns on and off, significantly impacts its efficiency and longevity. This issue leads to increased wear and tear, as the frequent cycling puts extra strain on the furnace’s components.
Over time, this can result in accelerated deterioration of parts like the blower motor and heat exchanger. This wear and tear not only shortens the lifespan of the furnace but also affects its ability to heat the home efficiently.
Moreover, short cycling leads to higher energy consumption. Since the furnace uses the most energy at startup, frequent cycling causes it to consume more fuel or electricity, leading to increased utility bills.
Short cycling can cause uneven heating in the home, as the furnace does not run long enough to distribute heat evenly.
Diagnosing Persistent Furnace Shutdowns
A furnace that frequently shuts down requires thorough troubleshooting to identify and resolve the underlying issue. The first step is to check the thermostat settings.
An incorrectly set thermostat can cause the furnace to turn off prematurely or not turn on at all. It’s essential to ensure the thermostat is set to ‘heat’ and the temperature is set higher than the current room temperature.
Another critical area is the pilot light or ignition sensor in gas furnaces. If the pilot light is out or the ignition sensor is dirty or faulty, the furnace may not be able to maintain a flame, causing it to shut down. Regular cleaning of the ignition sensor and checking the pilot light can prevent these issues.
The furnace’s control board is also a vital component to inspect. This board controls all the functions of the furnace and can be a source of problems if malfunctions.
External temperature fluctuations can impact furnace behavior, making it essential to consider insulation and thermostat placement for optimal furnace operation.
Learn More: Common Heatmor Outdoor Furnace Problems: Expert Solutions
Furnace Safety and Short Cycling
Furnaces are equipped with various safety mechanisms that can cause them to turn off as a precaution against potential hazards. One such mechanism is the high-limit switch, designed to shut down the furnace if it detects excessively high temperatures. This prevents overheating, which can damage the furnace and pose a fire risk.
The flame sensor is another critical safety feature, particularly in gas furnaces. It ensures that gas is not released without ignition, preventing gas buildup. If the sensor is dirty or faulty, it might incorrectly detect the absence of a flame, causing the furnace to shut off.
The furnace’s pressure switch is also vital for safety. It monitors the venting of exhaust gases, shutting down the furnace if it detects venting problems. This prevents the buildup of harmful gases like carbon monoxide within the home.
Learn More: Camper Furnace Not Working: Possible Causes + Solutions
Preventing Frequent Furnace Cycling
To prevent frequent cycling of a furnace, a combination of regular maintenance and strategic upgrades is essential. Regular maintenance, including cleaning air filters, inspecting the thermostat, and ensuring vents are not blocked, plays a crucial role in keeping the furnace running smoothly.
Professional inspections are also valuable, as technicians can identify and fix issues that may not be apparent to the average homeowner.
Consider replacing an old or inefficient furnace. Modern furnaces are more efficient and less prone to cycling issues.
Installing a smart thermostat can significantly improve furnace operations. These thermostats optimize heating cycles based on your habits and preferences, reducing unnecessary cycling. They also provide valuable data on furnace performance, which can help in identifying issues early on.
Read Also: How To Tell If Furnace Transformer Is Bad?